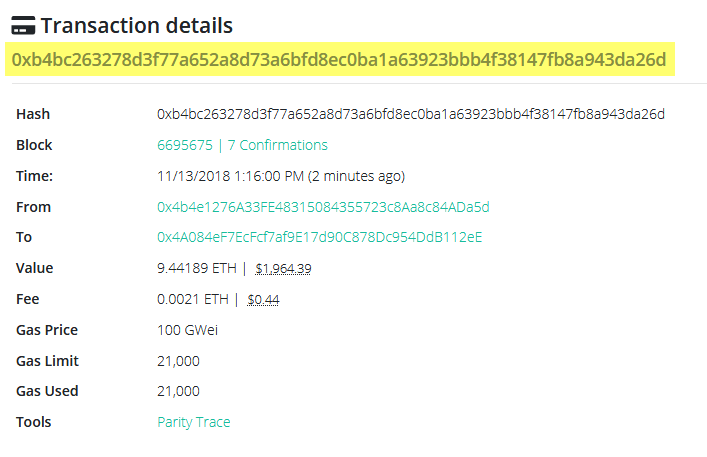
What is a Transaction Hash/Hash ID in Crypto?
Blockchain technology offers the realm of digital transactions great security and openness. A main characteristic of it is the transaction ID, sometimes referred to as a transaction hash. Anyone interested in cryptocurrencies must first understand transaction IDs as they are so important for checking the validity of transactions and guaranteeing openness inside blockchain systems.
Transaction ID and Tx Hash both stand for “Transaction Hash” (TxID). Made up of alphanumeric characters, it is essentially an identification number offered for a cryptocurrency transaction. This is only a fleeting fact on it. Then, what is a transaction hash/hash ID?? Every single transaction occurring on the cryptocurrency blockchain shows this unique identification.
What is a Transaction Hash/Hash ID??
Like a receipt, a transaction hash/ID—often shortened as tx hash or txn hash—is a unique identification used as evidence that a transaction was verified and entered to the blockchain. Often times, locating funds requires a transaction hash.
Created by running a hash function over transaction data including the sender’s address, the receiver’s address, and the amount of cryptocurrency being sent, transaction IDs are a unique string of characters.
Though it seems like a long string of arbitrary characters, every character in the transaction ID adds to its uniqueness. Usually generated by cryptographic hash techniques such as SHA-256 or RIPEMD-160, where any slight change in input data results in a significantly different hash output..
Designed to produce a unique fixed-size hash value from input data, SHA-256— Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit—is a cryptographic hash function. SHA-256 is used in blockchain transactions to generate a transaction ID from the transaction data, therefore providing a unique identification for that particular transaction on the blockchain and so guarantees data integrity and immutability.
RIPEMD-160 (RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation Message Digest-160) is a cryptographic hash function often employed to build shorter versions of public keys in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it produces a 160-bit hash value that forms the foundation for address generation and guarantees a better degree of security.
Transaction IDs also show key information like sender and recipient addresses, crypto amounts, and other details including notes or destination tags including other transaction records.
Importance of Transaction IDs
We will now discuss what a TxID, or Transaction Hash, might be used for now that we know what they are:
- Transaction Tracking and Verification: Simply entering this special code into a blockchain explorer is like utilizing GPS to determine whether your transaction has been finished or is still under progress.
- Record-Keeping: Another application of the TxHashes is record-keeping, whereby every transaction on the blockchain is logged. They record every element of every agreement, from a basic buy-off of coffee to the sale of a large skyscraper.
- Resolving Conflicts: Have you ever disagreed about a transaction in which everyone tells a different story? Say you know the TxID. In such situation, you will also realize that it serves as the last judge; it presents the facts with excellent accuracy, much as a Swiss watch, and leaves no room for discussion.
- Tax and Compliance Reporting: TxHashes are like a thorough road map indicating the movement of your digital money in taxes and compliance reporting. With the tax authorities investigating bitcoin transactions, they are absolutely necessary to ensure everything is in order.
Anyone can cross-reference transaction data using transaction IDs, hence improving openness and responsibility on blockchain systems.
Verifying the legitimacy of transactions and guarantees against illegal changes depend on transaction IDs. Users can verify that a transaction has been entered into the blockchain and track its development in real-time by referencing these special identities. Their digital assets must be safely transferred and received; hence this is absolutely necessary.
Understanding transaction IDs also helps users to locate these IDs and trace their transactions securely and transparently using blockchain explorers and bitcoin wallets. This is evidence of the ability of blockchain technology to offer an open and distributed framework for online transactions.
One can use a transaction hash for:
- Sending address
- Receiving address
- Amount
- Date and time
- Network fees
One can access transaction hash data by means of a block explorer, a website designed for searching the hash and displaying the ledger.
Each cryptocurrency asset runs on top of at least one blockchain among several blockchains. Looking up a transaction hash on a block explorer requires using the block explorer designated for that blockchain. For instance, BTC runs on the bitcoin blockchain; so, you must observe those transactions using a bitcoin block explorer. Operating on the Ethereum blockchain, ETH requires an e Ethereum block explorer to observe such transactions.
Knowing the blockchain a transaction was sent on helps you to view the transaction on the proper block explorer. Should you search a transaction hash on the incorrect block explorer, either nothing will show or the results will be incorrect.
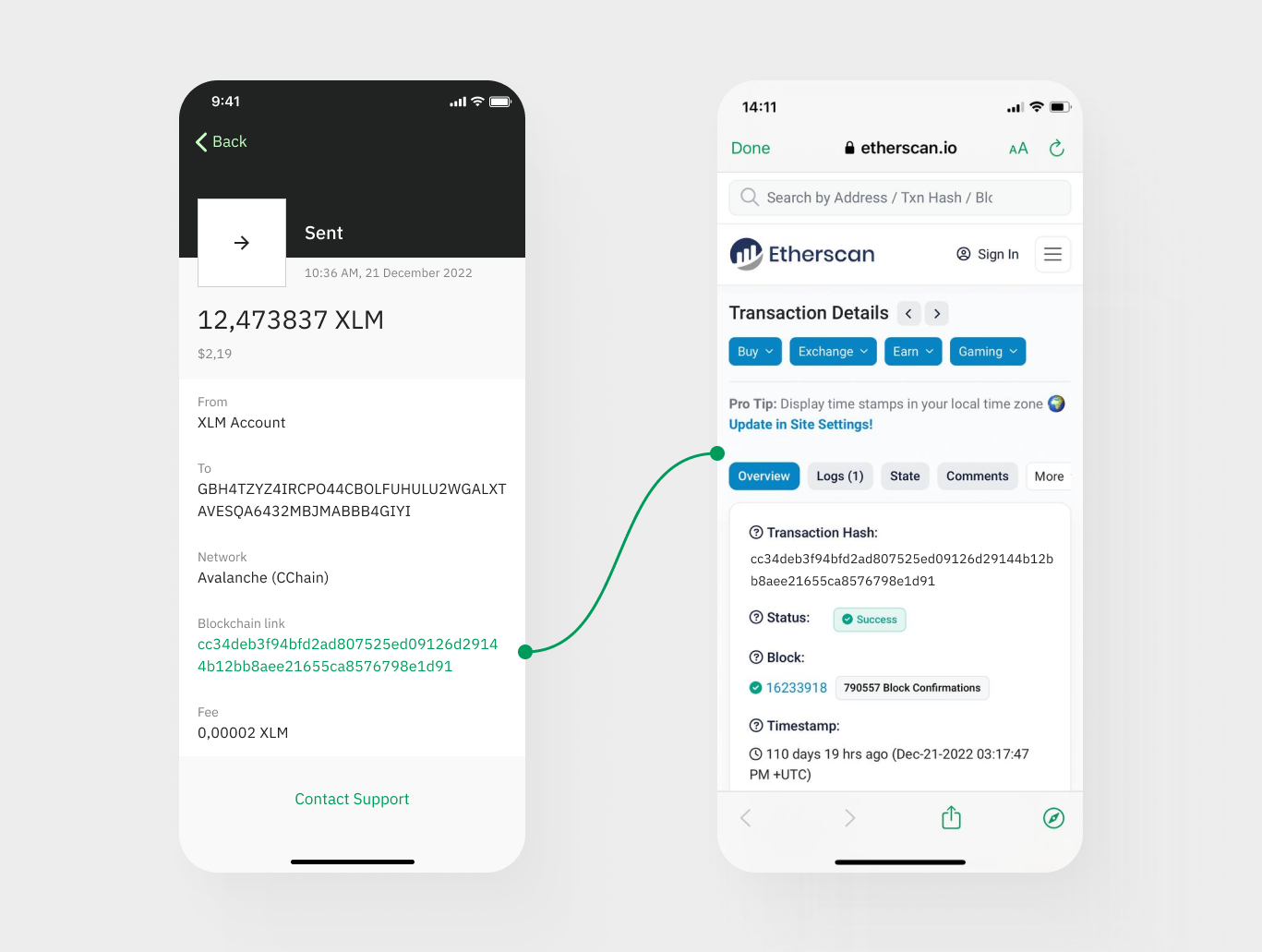
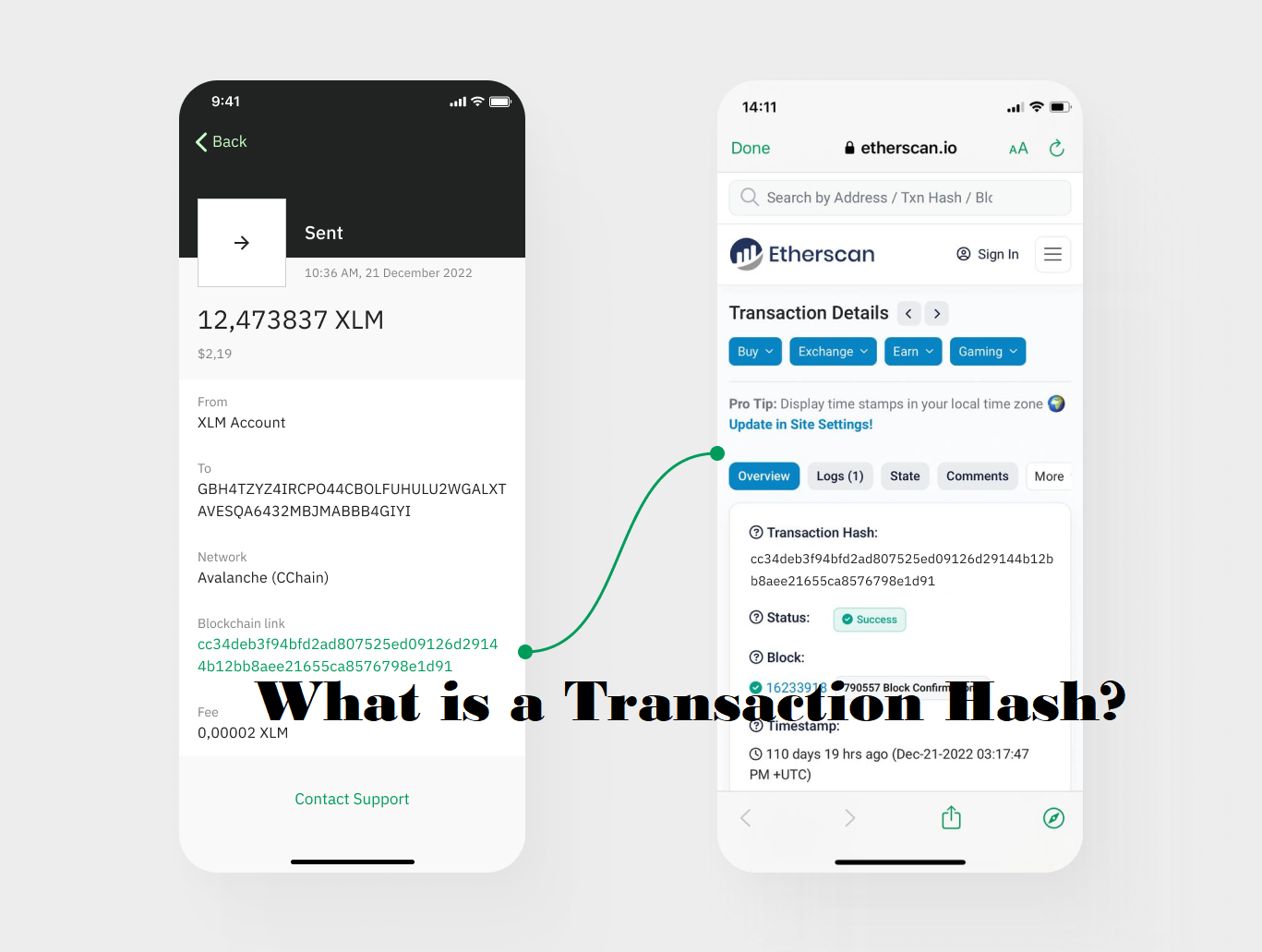
Is Giving Out a Transaction Hash Safe?
The public can access blockchain transactions generally. Sending money or coins to another address causes a broadcast transaction and generates a Tx Hash ID also. With the transaction ID, one may readily follow and record the state of a transaction. They will know all the details of the transfer, including the sender and destination addresses, the total amount sent, the date of the transfer, the height of the block, the costs related with it, and the number of confirmations. Since they do not include any personal information, we would want to exchange transaction hashes and IDs.
Best Privacy Practices
Adopting best practices helps to preserve privacy and security in view of the possible privacy issues connected with TXIDs.
- Using a different address for every transaction helps one to keep privacy. This makes linking events to a specific user more difficult for viewers.
- Mixing Services: Some consumers choose mixing services whereby their coins are combined with others to hide the transaction trail. These services are not advised for inexperienced users nonetheless, and carry some hazards.
- Selective Disclosure: Share your TXIDs only to reliable people. Publically sharing TXIDs reveals your connected addresses and transaction history.
- Privacy Coins: Consider adopting privacy-oriented cryptocurrencies with improved anonymity. These coins use different techniques to hide transaction tracks, so making it more difficult to connect events to users.
Risks and Constraints
TXIDs have certain drawbacks even if they have many advantages such proof of ownership, transaction verification, and double spending prevention. Transaction linkage, for example, allows an observer tracking a user’s TXIDs to perhaps track their transaction past.
Using shorter hashes that raise collision hazards adds still another constraint. A collision happens when two separate transactions produce the identical TXID, therefore causing possible transaction data misrepresentation or misunderstanding.
Finally, Texas ID disclosure can cause privacy issues. TXIDs are public hence anyone may find the transaction information including sender and recipient addresses as well as the transaction amount. Although privacy is more affected than security, many blockchain users give this great thought nonetheless.
Blockchain Transaction ID Explorer Tools
Blockchain explorers serve as search engines made especially for blockchain transactions. Just entering the transaction ID allows them to confirmations, search transaction data, and even spot possible problems. The capacity of these explorers to offer thorough analysis of every transaction helps to sustain the openness and confidence inside the network.
For both novice and experienced investors, blockchain explorers such as Etherscan, Blockchain.com, and BscScan provide real-time transaction data—a basic tool. The information at hand comprises the sender’s address, the recipient’s address, and transaction value.
Also Read: What is Transactions Per Second (TPS) in Blockchain? TPS Fully Explained
Other Transaction Identifiers
Apart from the transaction ID (TXID), which is the fundamental identification in a blockchain transaction, there are other identities that give pertinent background for on-chain transactions. These cover block height, block hash, and nonce.
Block Height and Hash
Block height in the context of a blockchain is the count of blocks before a given one. In the blockchain network, it provides a handy point of reference that enables users to ascertain the blockchain’s length at any one moment. Given each block’s linear, historical sequence, the block height offers a view of the blockchain’s development and expansion.
Conversely, the block hash is a distinct identity created for every block on the blockchain. Like the TXID, the block hash is generated by a cryptographic method that converts the data in the block into a set-length series of letters and numbers. Apart from being a distinctive identification for the block, this hash ensures the data integrity inside it. Any modification to the block data will produce a different hash, therefore suggesting possible data corruption or tampering.
Nonce and their Function
The process of mining fresh blocks on the blockchain depends much on the nonce, sometimes known as “number only used once.” Within blockchain technology, the nonce is a random number that miners can alter to generate a hash satisfying the particular criteria of the difficulty objective of the network.
The nonce guarantees blockchain security and integrity, therefore ensuring its duty. Miners run a computational race called proof-of- work by varying the nonce in search of a hash below the difficulty target of the network. The first miner that achieves this gets to add the new block to the blockchain; the nonce used to create the winning hash acts as evidence of their activity.
Final Thoughts
In essence, negotiating the world of digital transactions—especially in relation to cryptocurrencies—requires a knowledge of blockchain transaction IDs. Unique identities produced by cryptographic hash systems such as SHA-256 or RIPEMD-160 are transaction IDs, sometimes referred to as transaction hashes.
Verifying transaction authenticity, stopping double spending, and offering transparency and responsibility inside blockchain systems depend critically on transaction IDs. Although transaction IDs provide several advantages—including improved security and proof of ownership—it’s crucial to recognize related risks like privacy issues and possible limits like transaction linking and collision hazards.
Users can more successfully make blockchain transactions by following best practices for privacy and security and using extra transaction IDs like block height, block hash, and nonce, therefore guaranteeing a safer and more transparent digital transaction experience.







One Comment